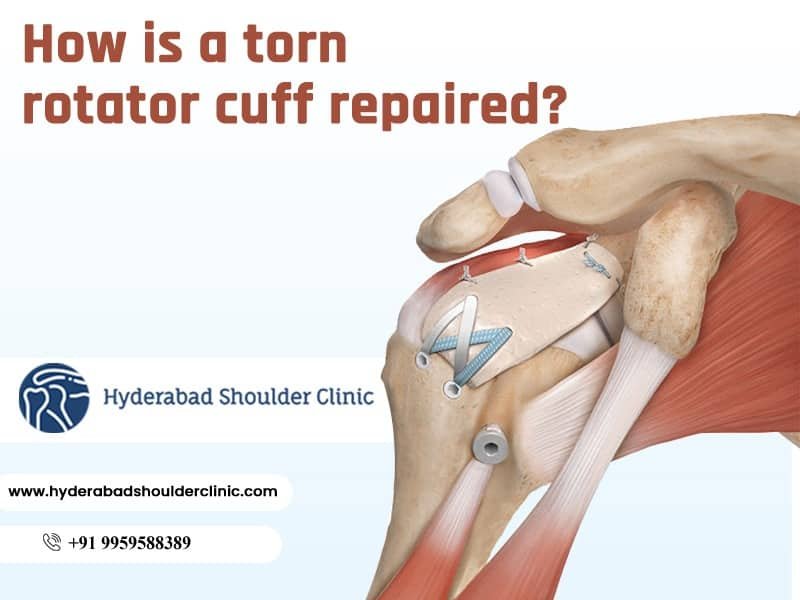
The rotator cuff is made up of muscles and tendons that hold the shoulder in place. This is one of the essential parts of the shoulder. Allows you to raise your hand and reach out. An injury to the rotator cuff can occur suddenly when falls on outstretched shoulders or develops over time due to repetitive activity. Degeneration and tearing of the rotator cuff can also be caused due to ageing.
Pain associated with rotator cuff tears usually occurs in the front and sides of the shoulder or upper arm and is often described as aching, burning. The pain usually occurs while moving overhead, but can progress to the point where the pain is present during everyday activities or wake the patient while they are sleeping.
A tear in the shoulder rotator cuff has the potential to cause pain and dangerous conditions and treatments for rotator cuff tears vary widely depending on the severity of the symptoms and signs. A person with a torn cuff may experience sudden (acute/ traumatic) or gradual (chronic) shoulder pain, with or without weakness.
Unfortunately, if the rotator cuff muscles are completely torn, they won’t heal on their own. Leaving them unattended can cause small tears progress to more significant tears and a progressive loss of movement and strength. The longer a large tear lasts, the bigger the tear and the more movement and strength is lost. The results of surgery tend to be better with small tears than those with larger tears The longer the crack is left, the less satisfactory the surgical results will be.
If your rotator cuff is injured, you may need surgery to repair it. This may include shaving bone spurs that impinge on the shoulder or repairing a tendon or torn muscle in the shoulder. Surgical techniques that are used for rotator cuff injury include open surgery, arthroscopy, or a combination of both. The goal of surgery is to restore function, the flexibility of the shoulder, and to relieve pain that cannot be controlled by other non-surgical treatments.
This article was provided by Dr Chandra Sekhar . B gives information about How is a torn rotator cuff repaired.
What is rotator cuff repair?

The rotator cuff is a combination of muscles and tendons that connect the bones of the upper arm, humerus and shoulder blade. The rotator cuff also holds the bones in the upper arm in the shoulder cavity. The rotator cuff muscles are of four: Infraspinatus, Supraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. Each of this muscle is connected to the shoulder bone by a tendon. Rotator cuff repair is the process by which a tear of one of these tendons is repaired.
Treatment options for a torn rotator cuff?

The fact that the torn rotator cuff may not be repaired does not mean that treatment cannot be considered, nor does it mean that people should choose to live with their condition.
Treatment options, both surgical and non-surgical. Non-surgical treatments include ice, anti-inflammatory drugs, cortisone injections, activity changes, and physical therapy.
People need to understand that even with a massive rotator cuff tear , there are still many muscles and tendons above the shoulder joint that can replace the damaged rotator cuff tendon. The focus of any treatment should be on therapeutic activities aimed at restoring the normal mechanisms of the shoulder joint.
Conservative treatment: Comprising rest, ice, and exercise are all that is only needed to recover from a rotator cuff injury sometimes. If your injury is severe and pain cannot be controlled with non-surgical methods, surgery may be needed.
Injection: If conservative treatment doesn’t relieve pain, your doctor may recommend steroid injections into your shoulder joint, if the pain is interfering with sleep, daily activities, or physical therapy. Although these injections are often temporarily useful, they should be used with caution as they can weaken the tendon and reduce the success of the operation.
Physical therapy: Physiotherapy is usually one of the first treatments your doctor may suggest. Exercises tailored to the specific location of your injury can help to restore strength and flexibility of the shoulder. Physical therapy is also an important part of the recovery process after rotator cuff surgery.
Surgery:

Even though you have an irreparable rotator cuff tear that does not mean surgery cannot be considered. Some surgeries may also be considered for irreparable tears of the rotator cuff. There are many types of rotator cuff surgeries , including:
Arthroscopic tendon repair: If you have rotator cuff tears, your doctor may recommend arthroscopic surgery to repair the tear. During the arthroscopic repair, the surgeon inserts a small camera called an arthroscope into the shoulder joint. The camera on the instrument displays an image on a television screen, and the surgeon uses this image to repair with miniature surgical instruments.
Arthroscopic repair is usually done on an outpatient basis.. Several arthroscopic techniques can be used to repair a different type of torn rotator cuff muscle, it depends on patient to patient condition.
Open tendon repair: In some situations, restoring the tendon by open method may be a better option. In this type of surgery, the surgeon works through a larger incision to reattach the huge damaged tendon to the bone. This operation needs a longer time. If you have a very large or complex tear, your surgeon may choose this method.
Tendon transfer: If the torn tendon is too damaged to attach to the arm bone, the surgeon may decide to use a nearby tendon as a replacement. If the rotator cuff tendon is chronically torn and twisted beyond repair, there may be an opportunity to transfer the adjacent tendon to replace the damaged rotator cuff.
Shoulder replacement: Badly injured rotator cuff may need shoulder replacement surgery. To increase the stability of the artificial joint, an innovative procedure (reverse shoulder arthroplasty) places the rounded sections of the artificial joints in the scapula and base in the arm bones.

Shoulder Debridement Surgery: In shoulder debridement surgery (abrasive arthroplasty), your surgeon performs a procedure to “clean” the shoulder. Shoulder debridement is usually performed as arthroscopic shoulder surgery. Your surgeon will use tools to remove damaged or inflamed tissue, smooth any uneven surfaces, and remove loose cartilage or other damage to the shoulder.
Partial Rotator Cuff Repair: If it is determined that the tear of the large rotator cuff cannot be repaired, tear reduction is possible. While this may not be a complete repair of a damaged tendon, sometimes even a partial repair will help restore function to the shoulder joint.
Reverse Shoulder Replacement: In situations where the shoulder joint becomes rheumatic and painful, and the rotator cuff is damaged beyond repair, certain types of shoulder replacement may be performed.
This surgery, known as a reverse shoulder replacement, is performed to change the mechanism of the shoulder joint in such a way that a functional replacement can be performed even if there is damage to the rotator cuff.
Conclusion:
Tears on the rotator cuff are a prevalent problem. The rotator cuff tear is finally an expected finding, especially as we get older. As humans entered the 60s and 70s, rotator cuff tears became a normal MRI finding.
After having a surgery, chances to reduce or relieve shoulder pain are excellent. However, surgery may not fully restore your shoulder strength. With time and physical therapy, you can regain your function, but you may still feel weak, stiff, or have chronic pain. It may take several months before you can exercise or engage in other activities that require shoulder strength and a variety of movements.
For more information on rotator cuff repair surgery and best treatment options on your condition, contact Dr Chandra Skehar. B at 91 9959588389.