It is estimated that more than 20% of the population currently have rotator cuff injuries. Many patients don’t even realize they have a rotator cuff injury, let alone seek treatment for it.
Some doctors recommend immediate surgery for rotator cuff injuries. The good news is surgery isn’t always necessary. Being aware of your injury is the best way to defend yourself.
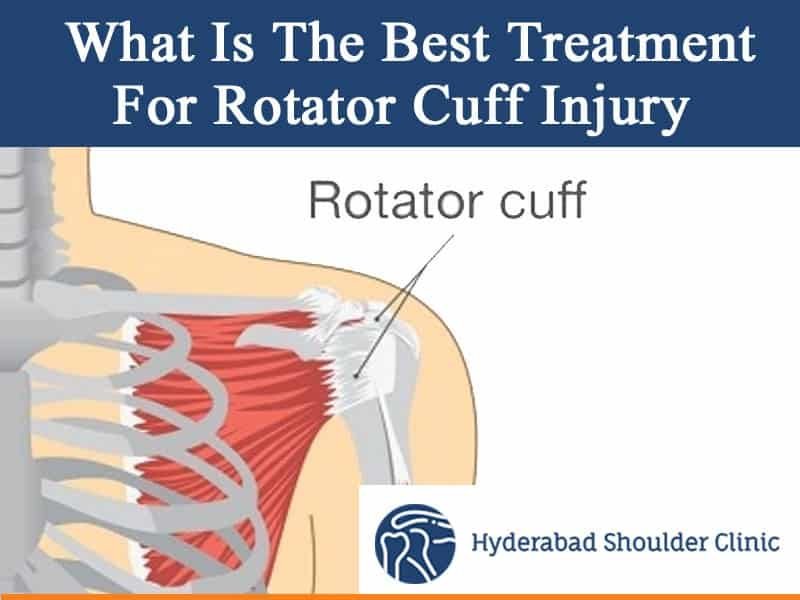
Rotator cuff injuries typically involve stretching or tearing of the rotator cuff, the muscles and tendons, that give movements to your shoulder. During trauma, the rotator cuff tendon (the thick tissue that connects muscle to bone) is often torn.
The most common point of the break is the supraspinatus tendon. Serious injury can cause multiple tendons and muscles to tear.
Let’s take a step by step approach to this problem so that you can make the right decisions about your treatment. Before that, let us see What a Rotator Cuff is.
What is a Rotator Cuff?

The rotator cuff is a general term that flows into everyday speech. Have you ever stopped and asked where your rotator cuff is? You may be surprised to learn that your rotator cuff is not one muscle, but a group of muscles and tendons that work together to stabilize your shoulder as you move.
Your rotator cuff is made up of the muscles and tendons in your shoulder that connect the bones of the upper arm to the shoulder blade. The rotator cuff holds the ball of the humerus firmly in the cavity of your shoulder. The term “rotator cuff injury” can mean many different things and includes any irritation or damage to your rotator cuff muscles or tendons. About half the time, rotator cuff injuries can be cured with physical therapy. However, surgery is sometimes needed to treat an injury.
Rotary cuff pain is one of the most common shoulder problems in adults. If your shoulder has pain and it prevents you from doing your daily activities, make an appointment with Dr Chandra Sekhar. B best shoulder specialist. He can help you identify the cause of your pain and then create a plan to help you heal and strengthen your shoulder so you can get back to doing the things you love.
Let us see treatment!
Treatment:

A thorough medical history and physical examination almost always yield the correct diagnosis. X-rays are mostly normal but an MRI provides a definitive diagnosis. This test clearly shows the muscles, inflammation, injuries, or tears.
Treatment focuses on treating pain and muscle regeneration to achieve the best possible function.
- Conservative treatment: It includes rest, ice packs, and physical therapy. Sometimes only this is needed to recover from a rotator cuff injury. If your injury is severe surgery may be required. Rest: Once you are aware of your injury, don’t press any further during rest using a clamp as a compression sleeve for your rotator cuff. When you are relaxing, avoid strenuous activities and relax your shoulders as much as possible.
- Ice: If there are swelling and inflammation, use an ice pack to manage it. Cold therapy calms the nerves and relieves swelling. If you have muscle stiffness, tension, or cramps, you can opt for a heat therapy package to heal the injury. Regardless of whether you are using a cold or hot therapy pack, make sure the temperature is right for your skin to prevent frostbite or burns.
- Medications: If the pain persists, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are highly recommended. NSAIDs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) can help. In its early stages, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs can provide benefits. However, to treat inflammation, it is essential to limit repetitive activities, and it is equally important to try to keep the elbows under the shoulders when using the hands.

- Physiotherapy: Physical therapy under the supervision of a shoulder specialist is the most essential step in treating a rotator cuff injury. Strengthening the rotator cuff muscles is vital to maintaining normal shoulder function. Several appointments with a physical therapist can help you learn exercises to relieve and prevent recurrent shoulder pain. Physical therapists may also try treatments to relieve pain and inflammation, including ultrasounds, electrical stimulation, and other treatments.
Physiotherapy is usually one of the first treatments your doctor may suggest. Exercises tailored to the specific location of your cuff injury can help restore flexibility and strength to your shoulder. It is also an essential part of the recovery process after shoulder surgery.
- Corticosteroid injections: If conservative treatment doesn’t relieve pain, your doctor may give steroid injections into your shoulder joint, if the pain interferes with sleep, daily activities, or physical therapy. Although these are often temporarily useful, they should be used with caution as they can weaken the tendon.
It is best to seek medical advice if pain persists or gets worse after using this conservative treatment. You should also monitor that your range of motion is normal. If movement is severely restricted and pain prevents you from carrying out daily procedures, this is an excellent time to make an appointment with your doctor. If other treatments don’t help, or if you have a large tear, your doctor may suggest surgery.
Surgery for Rotator Cuff injury:
The operation can be performed as either an open operation, a mini-open repair, or an arthroscopy operation. Open surgery is usually designed for large tears and involves making a large incision in the skin to perform the surgery. For mini-open repair, your surgeon will operate through a small incision. They will also use arthroscopy as part of the surgery. A surgical procedure (arthroscopy) uses a thin, flexible camera and special instruments to look inside and heal your shoulder joint.
Your surgeon will suggest to you what type of shoulder surgery is best for you. Rotator cuff injury treatment aims to relieve pain and give you as much movement as possible in the shoulder. However, recovery from a cuff injury can be a slow process. You may need to take a few weeks off, especially if you’ve had a tear repair.

- Arthroscopic tendon repair: In this procedure, the surgeon inserts a small camera (arthroscope) and instruments through small incisions to reattach the torn tendon to the bone.
- Open tendon repair: In some situations, open repair may be a better option. In this type of surgery, your surgeon will work through a larger incision to reattach the damaged tendon to the bone. But the drawback is long time for recovery and skin scar on the shoulder.
- Tendon transfer: If the torn tendon is too damaged to attach to the arm bone, the surgeon may decide to use a nearby tendon as a replacement.
- Shoulder replacement: Shoulder replacement surgery may be required if the rotator cuff is badly injured. To increase the stability of the artificial joint, an innovative procedure (reverse shoulder arthroplasty) places the rounded sections of the artificial joints in the scapula and base of the arm bones.
Conclusion:
The prognosis for rotator cuff injury depends on the type of injury. According to Dr Chandra Sekhar. B, half of the people with rotator cuff injuries recover through exercise and home care. This intervention relieves pain and increases freedom of movement. If there is more severe damage to the cuff, shoulder strength may not improve unless the injury is surgically repaired.
If someone believes they may have injured their rotator cuff or the injury seems to be getting worse, it is best to talk to Dr Chandra Sekhar. B Best Shoulder Surgeon in Hyderabad. Book your appointment by calling 9959588389.