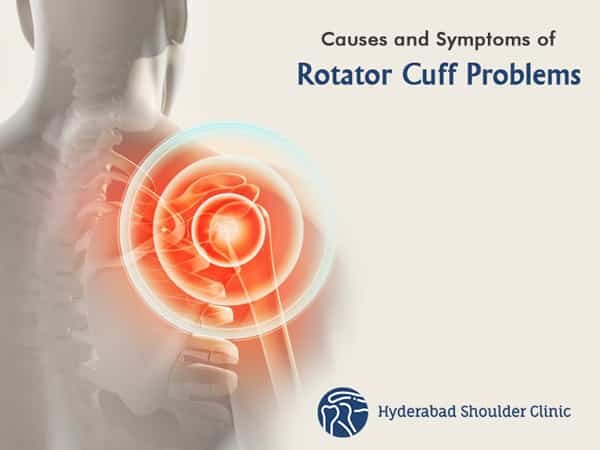
The rotator cuff comprises of four muscles and tendons that stabilize your shoulder joint and lets you lift and rotate arms.
Rotator cuff tear is the most common injury that occurs mainly in sports such as baseball, cricket, tennis, or when working as a painter or window cleaner. It usually happens over time due to regular use or when you repeat the same arm movements over and over.
Sometimes it can also happen when you fall on your arm or lift something heavy. There are two types of tears in the rotator cuffs. A partial tear takes place when one of the constituent muscles of the rotator cuff is damaged. The other is a complete tear in which it passes the tendon or pulls out the tendon from the bone.
Sometimes rotator cuff tear can occur due to a single injury. In this situation, we should give medical assistance as soon as possible. Extensive rotator cuff tears may require surgical repair, alternative tendon transfer, or joint replacement.
Dr Chandra Sekhar provides this blog about rotator cuff injury, causes, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment, as it is a common cause of pain and disability among adults.
What is a Rotator Cuff Injury?

A rotator cuff is made up of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint, holding the tip of the upper arm bone in a shallow shoulder cavity. Rotator cuff injuries can cause dull shoulder pain, which often gets worse when trying to sleep on the side of the affected shoulder part. It is one of the essential parts of the shoulder.
- Rotator cuff injury refers to the irritation of these tendons and inflammation of the bursa (usually the delicate layer) that lines these tendons.
- Rotator cuff tears occur when one of the tendons tear due to excessive use or injury.
What Causes Rotator Cuff Problems

There are two main reasons for rotator cuff Problems: injury and degeneration.
Acute Tear:
If you fall on an outstretched arm or lift an object that is too heavy with movement, then tear off the rotator cuff occurs. With another shoulder injury, This type of tear can occur, for example, fracture in the collarbone or shoulder dislocation.
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis:
Rotator cuff tendinitis is seen commonly in young athletes and middle-aged people. This occurs when the regular, healthy rotator cuff is injured or inflamed. This is often due to repetitive activities (such as tennis, painting, baseball, swimming, weightlifting, or volleyball).
Some chronic diseases are also associated with rotator cuff tendinitis. For example, diabetes and obesity can be risk factors. Obesity and smoking can also increase the chance of tear to their rotator cuff.
Degenerative Tear
Rotator Cuff Tendinosis:
Most tears are the result of tendon wear that slowly occurs over time. Of course, this degeneration happens with age. Rotator cuff tears problems are more common in the dominant hand. If you experience a degenerative tear in one arm, then you are more likely to suffer rotator cuff tear in the opposite arm.
Degenerative or chronic rotator cuff tears occur due to several factors they are:
Repeated stress: By repeating the same arm movements over and over, you can stress rotator cuff muscles and tendons. Tennis, rowing, baseball, and weightlifting are examples of sports where there is a risk of excessive tears. Much work and routine work can also cause damages.
Lack of blood supply: As the age grows, the blood supply to our rotator cuffs decreases. Without having a good blood supply, the body’s natural ability to repair damaged tendons is impaired. This can eventually cause tendon tears.
Bone spurs: As we get older, bone spurs (bone growth) often develops at the bottom of the acromion bone. When we raise our hands, the spurs rub against the rotator cuff tendons. This condition is referred to as a shoulder impingement that causes tendon weakening over time and increases the chance of fracture.
Risk Factors For Rotator Cuff Problems:

Rotator cuff problems can be acute or degenerative
Acute injuries are usually caused by one incident. They can be caused by lifting objects that are too heavy, falling, or discomfort in the shoulder. Middle-aged tend to suffer from this type of rotator cuff injury.
Degenerative injuries due to prolonged use: The most vulnerable people include:
- Athletes, especially tennis players, baseball players, rowers, and wrestlers
- People with the jobs which require repetitive movements of the shoulders, such as painters and carpenters
- People aged over 40 years at age
Symptoms:

Rotator cuff tears cannot directly cause pain, although they can cause acute injuries. Sometimes, someone can hear different popping sounds with weakness in the upper arm.
- Common rotator cuff injury symptoms include:
- Avoiding certain activities because they cause pain
- Difficulty in achieving various arm movements
- Trouble sleeping on the injured shoulder
- Pain or sensitivity to reach over the head
- Shoulder pain, especially at night
- Progressive shoulder weakness
- Problems with reaching behind the back
- Popping sensations when moves their hand
- Cracking sensations when moving the shoulder with injury, known as crepitus.
Sometimes the symptoms of rotator cuff injuries are not only due to the injury itself but also due to inflammation. This inflammation is usually in a protective bursa sac in the rotator cuff. This condition is known as bursitis.
If you experience any of the rotator signs or symptoms stated above for more than a week or lose the function of your hands, contact Dr Chandra Sekhar For best shoulder treatment.
How to Treat Rotator Cuff Problems?

Treatment depends on symptoms, age, and overall health, and also depends on the severity of the condition.
Treatment may include:
- Rest
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Strengthening and stretching exercises
- Ultrasound therapy
- Corticosteroid shot (injection)
- Surgery (for severe injuries or tears)
Your doctor can recommend surgery if your pain does not subside with non-surgical methods. Persistent pain is the primary reason for undergoing surgery. If you are very active and can use your hands for overhead work or sports, the doctor may suggest surgery.
Conclusion:
Problems with rotator cuff often occur, especially as we get older. Tear in the rotator cuff have finally become the expected discovery, even in people who have almost no pain in the shoulder. The good news is that most people feel better off with simple actions like avoiding certain activities and having physiotherapy for time to time.
For a detailed explanation of the surgical procedures that may be needed to treat your Rotator cuff tear problem, meet Dr Chandra Sekhar Shoulder surgeon, or contact us to 91 9959588389 to Book an appointment.