Shoulder instability is when the shoulder joint is too loose, causing it to move or slide excessively in the socket, resulting in partial or complete dislocation. This occurs when the shoulder’s structures, such as ligaments and tendons, are damaged or stretched. Chronic shoulder instability occurs when the head or top of the arm bone repeatedly slips out of the socket. It can be caused by a dislocated shoulder or repeated overhead motions in sports or activities. Damaged connective tissues in the shoulder make it easier for the joint’s ball to slip out of the socket, leading to shoulder pain.

Healthcare professionals recommended approaches to treat shoulder instability
Surgical Options for Treating Shoulder Instability
Based on the intensity, pain and cause of shoulder instability, several types of shoulder operations stabilise the shoulder. In most cases, arthroscopic surgery is preferred due to its minimal invasion and quicker healing periods. In extreme cases, open surgery is done where an incision is made in your skin, depending on the type of injury you have and the type of surgery needed. During the arthroscopic procedure, your surgeon will make small incisions in your shoulder called portals, via which a tiny camera is then placed in the portals. The surgeon can view the interior space of the shoulder. In the same session, the cause of instability can be corrected.
Physical therapy
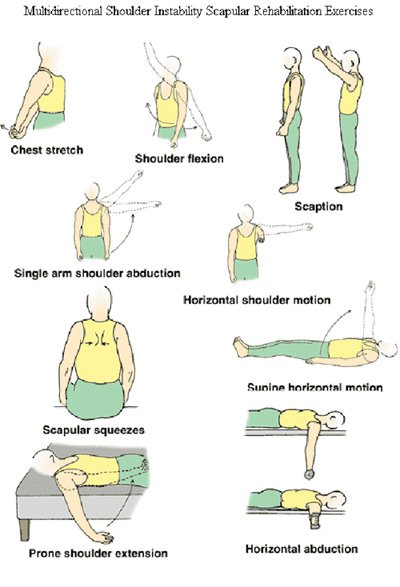
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint can provide stability.
- Exercises involving a range of motion could also be helpful.
- Regularly engage in exercises to strengthen shoulder muscles, especially the rotator cuff muscles, with a physical therapist recommending specific activities for your particular needs.
- A comprehensive fitness program focusing on strength, flexibility, and endurance is essential for maintaining a balanced musculoskeletal system.
- Maintaining good posture, particularly during shoulder-related activities, can enhance shoulder mechanics and decrease the likelihood of instability.
- It is advised to avoid placing the shoulder in extreme positions that may strain the joint and its surrounding structures.
- Warming up before physical activities is crucial to prepare muscles and joints for exercise demands.
Rest and activity modification
- Avoid activities that may worsen shoulder instability.
- Rest the shoulder to allow for healing.
- Ensure your workstation is ergonomically designed for prolonged sitting or computer use to promote good posture and minimise shoulder strain.
- Regular physical activity and a healthy weight can enhance joint health and reduce stress on shoulder joints.
Shoulder instability categories
- Traumatic instability: A dislocation occurs when the upper arm bone’s head is forced out of the shoulder socket, often resulting from a sudden injury like a dislocation.
- Atraumatic instability: Overuse or repetitive strain on the shoulder, often due to muscle imbalances, ligament laxity, or other anatomical factors, is not a specific injury.
Causes for shoulder instability
- Trauma or injury: Traumatic events like falls, collisions, or dislocations can cause damage to shoulder structures that stabilise it.
- Repetitive strain: Overuse of the shoulder, especially during overhead activities like throwing and swimming, can lead to atraumatic instability.
- Muscle weakness or imbalance: Instability in the shoulder joint can be caused by imbalances in the muscles surrounding it, with the rotator cuff muscles playing a crucial role.
- Ligament laxity: Specific individuals may have naturally more lax ligaments, which can increase their susceptibility to shoulder instability.
- Anatomical factors: Instability in the shoulder joint can be attributed to certain anatomical variations or abnormalities in its structure.
- Labral tears: Tears in the labrum can cause instability, a cartilage ring surrounding the shoulder socket.
- Genetic factors: The genetic predisposition to ligament laxity may contribute to shoulder instability.
- Previous dislocation: The risk of future shoulder dislocations may increase once a shoulder has been dislocated.
Surgical treatments for shoulder instability:
Shoulder instability is a condition where the shoulder joint is too loose, causing excessive movement in the socket, leading to dislocations or subluxations. Surgical procedures are considered when conservative treatments like physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are ineffective in stabilizing the shoulder.
Common surgical treatments for shoulder instability include:
- Arthroscopic bankart repair:
- This is a minimally invasive procedure performed using arthroscopy.
- The surgeon reattaches the torn labrum (a ring of cartilage around the shoulder socket) to the rim of the shoulder socket.
- Sutures or anchors are used to secure the labrum in place.
- Capsulorrhaphy(Capsular shift):
- In this procedure, the surgeon tightens or repairs the stretched or torn ligaments and capsules surrounding the shoulder joint.
- It is done to reduce the size of the shoulder joint cavity and improve stability.
- Laterjet procedure:
- A more complex procedure involves transferring a piece of bone and attached muscle from the shoulder blade to the front of the socket.
- The transferred bone helps to create a bony block that prevents the shoulder from dislocating.
- Remplissage:
- Often, this procedure is combined with another approach.
- It involves filling in and stabilizing the shoulder joint by moving and securing the infraspinatus tendon over the defect in the humeral head.
- Open bankart repair:
- It is similar to arthroscopic Bankart repair but performed through a larger incision.
- The surgeon repairs the torn labrum and capsule to improve stability.
- Rotator interval closure:
- This procedure involves tightening the rotator interval, a part of the shoulder capsule.
- Closing the rotator interval can contribute to the stability of the shoulder joint.
- Haglund’s procedure:
- This surgery addresses specific types of shoulder instability caused by bone abnormalities.
- It involves removing a small piece of bone from the shoulder blade to prevent impingement.
The surgical treatment for shoulder instability depends on the severity of the issue, the anatomical problems, and the surgeon’s experience. Postoperative recovery involves rehabilitation and physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and stability. Consultation with a qualified orthopaedic surgeon is crucial for the most suitable surgical approach.
Common symptoms of shoulder instability
Shoulder instability can manifest in various ways, with the severity of these symptoms varying from person to person.
- Recurrent shoulder dislocation: Individuals with shoulder instability may experience repeated dislocations, where the shoulder joint partially or wholly falls out of its socket.
- The sensation of looseness or slipping in the shoulder: Some individuals may experience a loose or slipping sensation in their shoulder, even without a complete dislocation.
- Pain: Pain in the shoulder joint, particularly during specific movements or activities, may be caused by stretching or injury of joint structures.
- Weakness: Instability can manifest as weakness in the affected shoulder, especially when lifting or carrying objects.
- Instability with specific movements: The instability may be more noticeable during specific movements, such as reaching overhead or behind the back.
- Clicking or popping sensation: Individuals with shoulder instability may experience clicking, popping, or grinding sensations in the shoulder joint.
- Difficulty lifting objects: Individuals with shoulder instability often struggle with lifting or carrying objects due to interference with the normal functioning of their shoulder muscles.
- Muscle spasms: The shoulder muscles may experience spasms as they attempt to stabilise the joint.
- Numbness or tingling: Shoulder instability can cause nerve compression or irritation, causing numbness or tingling in the arm or hand.
Symptoms of instability, such as recurrent dislocations, may fluctuate depending on activities and movements. If you experience these symptoms, seeking medical attention for a diagnosis and treatment is crucial. An orthopaedic specialist can conduct a thorough examination, possibly including imaging studies, to identify the underlying cause and recommend the appropriate course of action.
Shoulder instability can occur in individuals without any predisposing factors, and if symptoms like recurrent dislocations, looseness, or pain occur, it is crucial to seek medical evaluation. An orthopaedic specialist can assess the condition, determine the underlying causes, and recommend an appropriate treatment plan. The specific causes of shoulder instability can vary among individuals, and a thorough evaluation, including a medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies, is essential for developing an appropriate treatment plan. This evaluation is crucial for developing a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
These precautions are general guidelines and may not cover all individual situations. Follow your healthcare professional’s advice and recommendations for shoulder instability treatment. They may tailor a plan based on your needs and shoulder instability characteristics. If you experience symptoms like recurrent dislocations or shoulder looseness, seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
About Dr Chandrasekhar
- First orthopaedic surgeon in entire South India to perform Arthroscopic Latarjet procedure. This surgery is considered to be a highly advanced surgery for the treatment of shoulder dislocation problems. Currently, only a handful of surgeons are performing this surgery worldwide.
- Credited with doing the first Arthroscopic AC joint (collar bone joint) reconstruction in both Telangana and Andhra Pradesh states.
- The first surgeon in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh states to perform Arthroscopic Superior Capsular reconstruction. In this procedure, tissue from the thigh of the patient is taken to repair the shoulder’s badly damaged rotator cuff muscles by endoscopic surgery.
- Performed Live surgery during the National Conference Shoulder workshop of the Indian Orthopaedic Association 2015 at Jaipur, Rajasthan. Dr. Chandrasekhar is credited with doing the first Reverse Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Andhra Pradesh.
- Dr. Chandrasekhar is credited with doing the first Arthroscopic Fixation Acromioclavicular Joint (Collar Bone Joint) in the combined state of Andhra Pradesh.
- Dr Chandrasekhar was honoured as the organising Chairman for the workshop on Shoulder Arthroscopy at the National Conference 2014 of the Indian Orthopaedic Association.
- Invited by the Govt. Djibouti, Africa, to provide treatment to their patients in 2014.