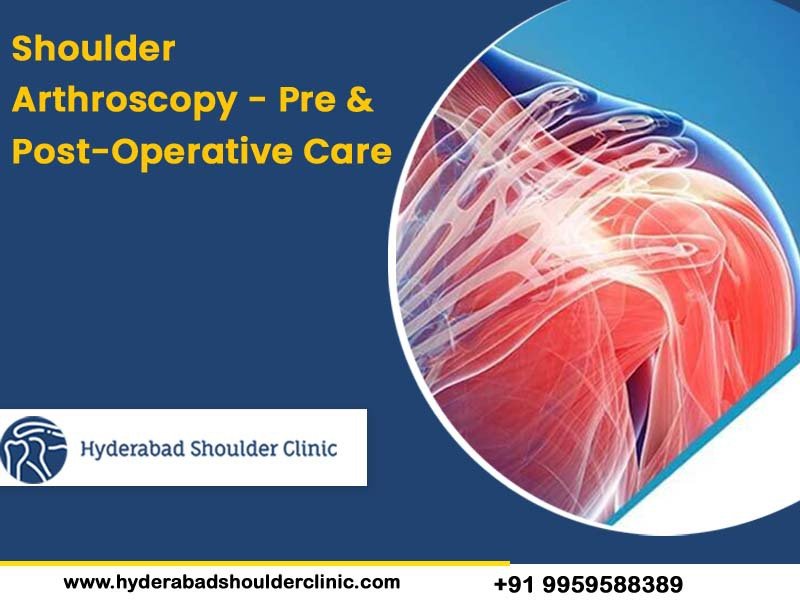
The shoulder joint is one of the most complex and critical joints in the body. It is often referred to as the ball and socket joint, where the upper arm bone known as the humerus locks into the shoulder blade known as the scapula. These bones are connected with numerous tendons and muscles to make up a joint and help it to rotate in multiple directions.
The three important bones in the shoulder joint are the Clavicle (collarbone), Scapula (shoulder blade) and Humerus (Upper arm bone), surrounded by muscles, ligaments and tendons. Shoulder arthroscopy is an invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose or repair the tissues surrounding or inside your shoulder joint.
Planning for surgery: Preoperative Care
- The orthopaedic surgeon first evaluates your general health to confirm that you don’t have any medical issues before the surgery. If you have specific health risks, you need a broad, progressive assessment before surgery. If you are taking any medications, inform your orthopaedic surgeon. Some of those medicines need to be stopped before surgery, according to the doctor’s recommendation.

- The doctor can order various tests to ensure surgery safety, including blood tests, electrocardiograms, and chest x-rays.
- You will receive specific instructions about the surgery from the doctor before the operation. Follow the instructions regarding when you should arrive for your surgery, particularly when you refrain from eating or drinking before your operation.
- One of the anaesthesia team members will discuss anaesthesia options with you before surgery. Regional nerve blocks are usually used to numb your arm and shoulder during shoulder arthroscopy. Anaesthesia is given at the neck’s base or top of shoulder, i.e at the location of the nerves which control your feeling associated with the shoulder and arm.
- In most cases, an arthroscopic procedure lasts less than an hour; in some cases, the procedure’s duration depends on the diagnoses and repairs your surgeons make.
How is shoulder arthroscopy done?
Most arthroscopy procedures are carried out in an outpatient setting. A few incisions less than one centimetre each are made to insert essential arthroscopic instruments. To see the joint during surgery, the surgeon fills the joint with clear liquid. The arthroscope inserted has a camera head to view inside the joint and repair the damaged part precisely. Depending upon the type of shoulder surgery performed, you might have to wear a sling or an immobilizer.

Symptoms you may experience after the surgery:
After surgery, you will be rested for a while before discharge. The below are typical symptoms people experience after surgery, and they will disappear in the next 12 to 20 hours. The symptoms you may notice are as follows:
- Hand and shoulder become immobile
- A numb feeling in your hand and shoulder
- Swelling
- Voice may become hoarse
- Drooping eyelids
Post Operative Care:
Your shoulder surgeon will give you specific instructions about the care you need to take following the procedure, such as moving your arm after the procedure.
- It may take several weeks or several months to resume full functioning of the shoulder after surgery and mainly depends on the type of surgery.
- To relieve pain and swelling, doctors suggest taking rest and using icing the area and anti-inflammatory medications.
- After the surgery, make sure you keep the surgery area dry for at least 3 – 5 days, so take care while you bathe.
- Change the dressings frequently. The patients usually perform light exercise after one week.
You should not move your shoulder actively during the first two weeks after surgery. As soon as you begin treatment following your first postoperative appointment, you will be provided with specific guidelines on how to continue activities. Therapy can be uncomfortable at times in the beginning. It is recommended not to lift, carry, push or pull anything heavy until four months post shoulder arthroscopy.
Orthopaedic Improvements with arthroscopic shoulder surgery:
Shoulder Arthroscopy without repair:
- Blanket Repair: Recurrent shoulder dislocation
- Debridement of partial rotator cuff tear: calcific tendonitis, labrum or biceps ligament
- Mumford procedure: Distal clavicle resection (a procedure to treat shoulder impingement)
- Subacromial decompression: It is an arthroscopic procedure that is performed to loosen the coracoacromial arch’s ligaments and the acromion’s undersurface.

- Synovectomy or bursectomy: it is a procedure to remove synovial tissue around the joint.
You will use your shoulder immobilizer for any of these surgeries to feel comfortable and then stop using it when you are ready. It varies depending on the surgery. When you feel comfortable, you may need strengthening exercises, which take around 2 to 3 weeks post-surgery. Early pendulum exercise and passive range of movement can be done in a few months after surgery. As a result of this exercise, your active range of motion will increase.
For more detailed information, consult Dr Chandra Sekhar, the best shoulder surgeon in Hyderabad. Call +91 99595 88389 to make an appointment right away.